Event: Joint ETSI SDG Ecosystem Day
Date: November 26, 2025
Location: Webinar (organized by ETSI)
Participant organizations: UBI, UoP, PNET, REDHAT
Presenter: Anastasis Poimenidis (UBI)
Projects: ACROSS HEU and P2CODE (UBI is the technical coordinator of both projects)
What happened in this webinar?
A consortium of partners from the ACROSS and P2CODE projects appeared in this event with a proof-of-concept demonstration that showcases how an open orchestration platform exploits standardized service runtime management APIs to perform various types of critical service reconfigurations to increase the performance of the deployed services, improve their security uptake, or move service components on demand for better resource management.
The event started with an introduction to service lifecycle management, emphasizing the various lifecycle stages and how standardized APIs are carefully designed to manage these stages. Then, the presenter highlighted that modern AI solutions provide advanced decision making around services that could only be leveraged if one could programmatically tune service runtime, therefore allow AI engines to properly close the loop.
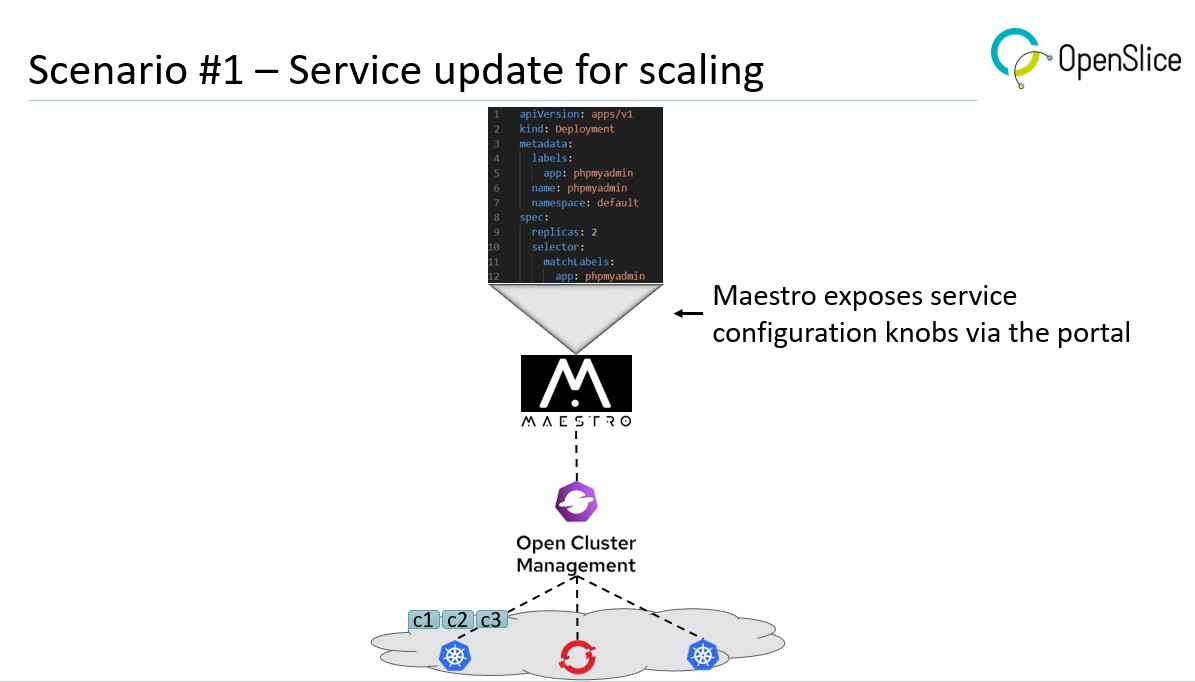
Next, the presenter introduced three service runtime update scenarios, each covering different runtime aspects. Before demonstrating these scenarios, the presenter explained the setup of the demonstration, which consists of two orchestration platforms, i.e., Maestro and OpenSlice, that belong to the ETSI OpenSlice Software Development Group (SDG) as well as an open cloud orchestration platform by RedHat titled Open Cluster Management (OCM). A short demonstration of this setup was provided, showing the service catalogs of the two orchestrators along with the state of the OCM cluster, before the execution of the three main scenarios.
Then, scenario #1 was presented, focusing on “Real-time updates for service scaling”. In this scenario, Maestro exposes service configuration via a portal, allowing users to tune the compute characteristics of a running service. The demonstration shows how the user tweaks the number of replicas of a service component to scale up its resources when needed.
Next, Scenario #2 was unfolded highlighting “Real-time updates for service security”. In this scenario, an attacker sends malicious traffic towards a deployed service. The developer of the service creates an updated version of the service with built-in traffic filtering and instructs Maestro to roll out this new version on the fly, without tearing the service down.
The third Scenario discusses a case that allows users to move service components from one cluster to another without tearing the service down. In this scenario, Maestro exposes cluster metadata via a portal, allowing users to tune the labels associated with each service component, thus affecting the placement of each component across the OCM clusters.
The presentation concluded with some useful information on the open-source systems used for this PoC along with references to their websites and software repositories.
What was proposed in this webinar?
This PoC proposes a series of service runtime operations – triggered via standardized APIs – that allow users to tune running services without disrupting their runtime. This is possible via a modern service orchestration platform based on Maestro, ETSI OpenSlice, and RedHat’s OCM that exposes these APIs via TMForum endpoints. The PoC emphasized how useful these APIs are, not only for improving the performance of the deployed services, but also for providing advanced security and better resource management in real world environments.
What will be adopted/or what will be considered by ETSI?
In this PoC, the ETSI OpenSlice platform acts as a middleware between the Maestro multi-domain service orchestrator and RedHat’s OCM platform. OpenSlice exposes OCM to Maestro using TMForum APIs at the resource level via TMF 634, 652, and 639 as well as the service level via TMF 633, 641, and 638 APIs. Maestro utilizes the service-level TMForum APIs to consume the exposed OCM and perform direct management of OCM resources via a dedicated Maestro-OCM channel.
This PoC proves how a combination of industry-grade TMF APIs with large scale open-source projects, such as RedHat’s OCM, can work in tandem to provide useful solutions for modern service management. This work also proves that ETSI SDGs conduct meaningful development activities which create solutions around large community projects of high impact.
PoC business value
Service providers that wish to manage their services’ runtime without delving into low-level consoles and applying technology-specific commands would find this PoC really valuable, as the PoC demonstrates how service updates can be easily done with a handful of steps via a user-friendly portal, leveraging technology-agnostic standardized APIs under the hood. Moreover, this PoC creates value for smart AI solution providers who wish to integrate their intelligence decision engines with the underlying infrastructure leveraging standardized APIs that will increase the adoption and interoperability of their solutions.
Related material
 The PoC demo presentation, detailing the service update scenarios and orchestration workflow, is available here: SDG_ED_OSL_Zero-touch end-user service update mechanisms via an open orchestration platform
The PoC demo presentation, detailing the service update scenarios and orchestration workflow, is available here: SDG_ED_OSL_Zero-touch end-user service update mechanisms via an open orchestration platform The corresponding demonstration video is available on the ACROSS YouTube channel: https://youtu.be/oM0WIWzNw1M
The corresponding demonstration video is available on the ACROSS YouTube channel: https://youtu.be/oM0WIWzNw1M
Find out more about each of the ACROSS test cases here: https://across-he.eu/video-clips/